ZGC - Concurrent Class Unloading
One feature ZGC is currently missing is class unloading before java 12 versions. This should be implemented. Due to the latency sensitive nature of class unloading, this operation should be performed concurrently.Concurrent Class Unloading Released in JDK 12 for ZGC
The Z Garbage Collector now supports class unloading. By unloading unused classes, data structures related to these classes can be freed, lowering the overall footprint of the application. Class unloading in ZGC happens concurrently, without stopping the execution of Java application threads, and has zero impact on GC pause times. This feature is enabled by default, but can be disabled by using the command line option `-XX:-ClassUnloading`.
Traditional Class Unloading VS ZGC Concurrnet Class Unloading
Traditional Class Unloading
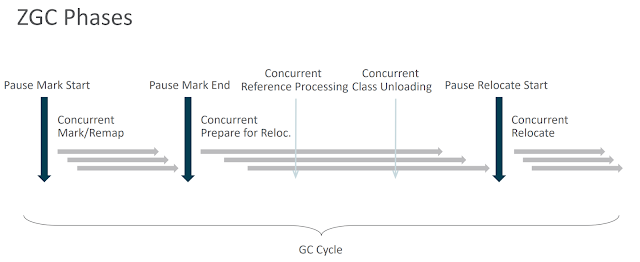
Step 1: Marking (concurrent)Mark metadata (classes, CLDs) when marking objects
Step 2: Reference processing (STW)
Need to know what is reachable from finalizers before class unloading
Step 3: Unloading (STW)
Unload code cache
Unload metadata
ZGC Concurrnet Class Unloading
Step 1: Marking (concurrent)Mark metadata (classes, CLDs) when marking objects
Mark both strong and final reachable graphs
Step 2: Reference processing (concurrent)
Already know what is reachable from finalizers before class unloading
Step 3: Unloading (concurrent)
Unload code cache
Unload metadata
Shenandoah: A Low-Pause-Time Garbage Collector:
Added a new garbage collection (GC) algorithm named Shenandoah which reduces GC pause times by doing evacuation work concurrently with the running Java threads. Pause times with Shenandoah are independent of heap size, meaning you will have the same consistent pause times whether your heap is 100 MB or 100 GB or 1TB.Modern machines have more memory and more processors than ever before. Service Level Agreement (SLA) applications guarantee response times of 10-500ms. In order to meet the lower end of that goal we need garbage collection algorithms which are efficient enough to allow programs to run in the available memory, but also optimized to never interrupt the running program for more than a handful of milliseconds. Shenandoah is an open-source low-pause time collector for OpenJDK designed to move us closer to those goals.
Shenandoah trades concurrent cpu cycles and space for pause time improvements. We've added an indirection pointer to every Java object which enables the GC threads to compact the heap while the Java threads are running. Marking and compacting are performed concurrently so we only need to pause the Java threads long enough to scan the thread stacks to find and update the roots of the object graph.
The Shenandoah algorithm is described in depth in this PPPJ2016 paper.
As experimental feature, Shenandoah will require -XX:+UnlockExperimentalVMOptions in the command line. The Shenandoah build system disables the build on unsupported configurations automatically. Downstream builders may choose to disable building Shenandoah with --with-jvm-features=-shenandoahgc on otherwise supported platforms.
To enable/use Shenandoah GC, the following JVM options will be needed: -XX:+UnlockExperimentalVMOptions -XX:+UseShenandoahGC.



0 Comments